Can You Have DKA Without High Blood Sugars?
By Jennifer Alvey
 Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially fatal complication of diabetes typically associated with dangerously high blood glucose levels. However, this is not always the case, specifically for those who take a new class of diabetes drugs called SGLT-2 inhibitors.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially fatal complication of diabetes typically associated with dangerously high blood glucose levels. However, this is not always the case, specifically for those who take a new class of diabetes drugs called SGLT-2 inhibitors.
People with diabetes who are on insulin treatment should be keenly aware of the dangers of diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. Indeed, many people with type 1 diabetes find out their diagnosis because they land in an emergency room in a state of diabetic ketoacidosis.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) occurs when someone does not have enough insulin in their body. Because there is not enough insulin to allow glucose to enter the body’s cells from the blood to be used for energy, the body responds by burning fat.
When this happens, ketones are produced, which can build up in the bloodstream. Ketones are acidic, so when ketone levels get too high, the blood can become acidic, which affects the function of the brain and other organs, and can be life-threatening.
Can you have diabetic ketoacidosis without high blood glucose levels?
Yes, it is possible to enter a state of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) without high blood glucose levels (also known as serum glucose levels).
 While people often associate diabetic ketoacidosis with high blood glucose levels, many don’t realize that they can become ill from ketoacidosis when their blood glucose level is under 240 mg/dl. A rare type of diabetic ketoacidosis, called euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (EDKA), occurs when blood glucose levels are not elevated, but there isn’t enough insulin in the body to prevent the breakdown of fats. Although cases of EDKA have occurred in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, type 1 patients are at higher risk for diabetic ketoacidosis than type 2 patients.
While people often associate diabetic ketoacidosis with high blood glucose levels, many don’t realize that they can become ill from ketoacidosis when their blood glucose level is under 240 mg/dl. A rare type of diabetic ketoacidosis, called euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (EDKA), occurs when blood glucose levels are not elevated, but there isn’t enough insulin in the body to prevent the breakdown of fats. Although cases of EDKA have occurred in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, type 1 patients are at higher risk for diabetic ketoacidosis than type 2 patients.
Since the introduction of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, emergency rooms have seen an increase in cases of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Current estimates peg EDKA cases at 2.6% to 3.2% of all DKA cases seen in emergency rooms – though this percentage might be low due to underreporting.
SGLT-2 inhibitors: A new cause of rare DKA called euglycemic DKA
SGLT-2 inhibitors, sold under the brand names of Jardiance, Invokana, Farxiga, and Steglatro, help reduce blood glucose by preventing reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys. Instead, the body gets rid of the excess glucose through the urine. It is important to note that the FDA has approved SGLT-2 use for people with type 2 diabetes only.
Euglycemic DKA can arise from prescribing SGLT-2 inhibitors off-label to people with type 1 diabetes
Some physicians, however, have prescribed SGLT-2s off-label to people with type 1 diabetes. Many people taking both insulin and an SGLT-2 benefit from lower glucose levels, fewer post-meal ups and downs, and weight loss, all without an added risk for hypoglycemia.
Once a SGLT-2 drug enters the picture, though, the risk of euglycemic DKA is 5-10% higher for people with type 1 diabetes than those not taking that medication.
Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis is much trickier for people with diabetes to discern, though, because the classic tip-off of sustained, elevated blood sugars is absent. Blood sugar is below – sometimes well below – 240 mg/dl.
One recent case study described a person with type 1 who was experiencing euglycemic DKA with blood sugar around 75 mg/dl.
When to check for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
If high blood sugar does not alert people with type 1 to check their ketone levels, what should they look for instead?
Classic diabetic ketoacidosis symptoms:
According to Dr. Charles Alexander, a Pennsylvania-based clinician and medical advisor to diaTribe, euglycemic DKA presents with many similar symptoms of classic DKA, including:
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Abdominal pain
-
Excessive thirst
-
Feeling of being unwell or weak, without any known reason
-
Lethargy
-
Loss of appetite
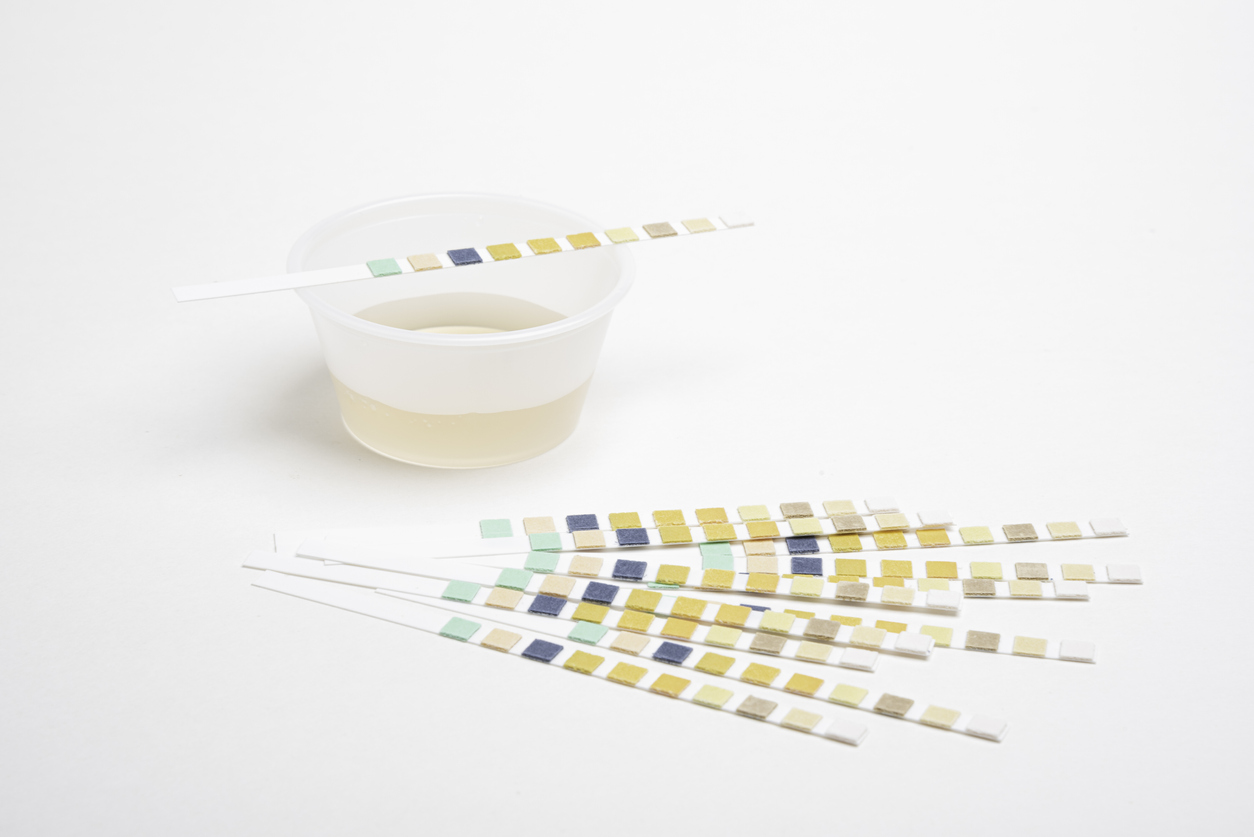 The importance of testing ketone levels
The importance of testing ketone levels
Alexander strongly suggests that people with type 1 who take an SGLT-2 check their ketone levels every morning. This suggestion is in line with the consensus standards issued by leading clinicians worldwide (including Alexander) on managing the risk of DKA in people with type 1 who take SGLT-2s.
At the first sign of any type of diabetic ketoacidosis, one should test ketone levels, even if blood sugar levels are within range. From ketone blood meters that measure BHB to urine strips that measure AcAc to meters that measure breath ketones, here is a primer on the most effective ways to test ketone levels.
It’s possible to check ketone levels with a simple, over-the-counter urine test strips or a ketone meter.
If you see elevated ketones, start hydrating aggressively as able, suggests Dr. Julie Hendrix, an endocrinologist in private practice in Franklin, Tennessee. She says it’s also important to take insulin and to consume a fast-acting carbohydrate, ideally a glucose-containing fluid such as apple juice.
SGLT-2 inhibitor drugs: The trigger, not the cause, of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (EDKA)
Typically, taking an SGLT-2 by itself is not what triggers an episode of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Other factors combine with the action of SGLT-2s to act as triggers.
Factors that contribute to euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (EDKA)
Many factors are related to some type of so-called starvation (when the body is unable to use, or does not have enough carbs for energy), such as:
-
Fasting
-
Not able to eat due to illness
-
Acute viral or bacterial infections
-
Following a low carbohydrate or ketogenic diet
-
Insulin pump malfunctions or missed insulin doses
-
Surgery
-
Pregnancy
-
A significant increase in exercise length or intensity
What to do in the event of euglycemic ketoacidosis (EDKA)
The idea of both taking insulin with normal blood glucose levels, and consuming carbs if diabetic ketoacidosis is suspected, are highly counterintuitive to most people with type 1. But without enough insulin and glucose, ketone levels will continue to rise, even if blood sugars are in range.
Consuming carbohydrates with insulin helps switch the body back to seeking energy from glucose, rather than fat. That fuel switch stops the liver from making glucose from fat, which halts ketone overproduction.
When persistent vomiting is present, all bets are off: seek IV hydration and medical treatment immediately.
Euglycemic ketoacidosis (EDKA) at the emergency room: Case studies
Not long after the drug Invokana went on the market in 2013, people with both type 1 and type 2 started showing up in emergency rooms with euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis.
Because EDKA is quite rare and health care providers had been taught that diabetic ketoacidosis only occurs when blood glucose levels are high, many emergency room professionals were deceived by blood sugar that was in a normal or slightly elevated range, and initially dismissed the possibility of diabetic ketoacidosis. Eventually euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis was diagnosed, but many more hours passed than would have if high blood sugar had been present.
Emergency room physicians have written many case studies about euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis since then:
-
One person, originally diagnosed as having type 2 and taking an SGLT-2, presented at the emergency room with a blood serum glucose level of 75 and had not eaten in two days. Her labs indicated a transition to LADA, as well as being in euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis.
-
A teenager with type 1, on an insulin pump but not taking SGLT-2s, presented at the emergency room with an initial glucose of 109. She had been vomiting intermittently for the previous 24 hours. Ultimately, she was diagnosed both with appendicitis and with EDKA.
-
A man in his 60s with type 2 was initially treated for a stroke that was evident on a CT scan. On the fifth day of his hospital stay, he became quite drowsy and was suddenly breathing rapidly. Bloodwork revealed severe acidosis, ultimately attributed to the Jardiance he had taken for years.
Many of these case studies stress that all people with diabetes who take SGLT-2s should be considered as potentially in DKA if they come to the emergency room, and that appropriate laboratory tests be run to confirm or rule out that diagnosis.
What to do if you're being denied treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis in the emergency room
Unfortunately, not every emergency room professional knows what EDKA is, or will know to order the correct lab tests to detect it.
It’s a very frightening prospect—you’re in the hospital because you know you are very ill, and have a good idea why, but your input is dismissed and you are not receiving the correct treatment.
In "Lessons Learned from A Scary Visit to the Emergency Room," Stefany Sheehan, the parent of a child with T1D and member of the board of trustees at Joslin Diabetes Center, breaks down her daughter’s experience with EDKA after taking an SGLT-2 inhibitor.
If you’re headed to the emergency room, contact your endocrinologist beforehand
Alexander suggests notifying your endocrinologist that you are going to the emergency room, so that they will be able to call the emergency room to discuss your situation and advise the emergency room staff. You can also ask the emergency room staff to call your endocrinologist.
You can also take copies of articles with you to give to your emergency room team if necessary. In addition to letting emergency room personnel know you are well educated about your diabetes, you may also save them time doing research about EDKA and SLGT-2 inhibitors.
If you cannot get through to the medical team in the emergency room, ask them to call an endocrinologist from the hospital to consult, if there is one available.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (EDKA): The bottom line
The specter of any type of DKA is concerning to people with insulin-treated diabetes. Understanding how it can happen, how to detect it early, and how to advocate for yourself should help those taking SGLT-2s keep themselves healthy and far away from a DKA emergency.
Further reading about the dangers of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA):
Photo credits: iStock